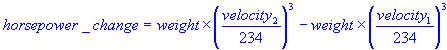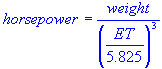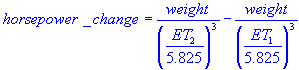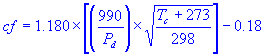Horsepower Equations Calculator
Automobile Car Truck Design Formulas
Problem:
Solve for rotating horsepower.
Enter Inputs:
Can you share this page? Because, it could help others.
Solution:
Solution In Other Units:
Input Conversions:
Change Equation or Formulas:
Tap or click to solve for a different unknown or equation
| Engine horsepower estimate using quarter mile elapsed time Includes plot and graph |
| Rotating horsepower | |
| Torque | |
| Speed - revolutions per minute (rpm) |
Background
Rotating horsepower is a crucial concept in mechanical engineering. It refers to the power a rotating object, such as an engine crankshaft, delivers. The equation that connects horsepower, torque, and rotational speed incorporates a constant, 5252, pivotal for the conversion, making understanding its use essential for calculating engine performance, among other applications.
Equation
The fundamental equation to solve for rotating horsepower (HP) given torque (T in lb-ft) and speed (RPM) is:
HP = Torque x Speed (RPM) / 5252
This relationship is derived from the definition of horsepower and the unit conversions necessary to reconcile the measurements involved.
How to Solve
- Ensure the units are correct: Ensure that torque is in pound-feet (lb-ft) and speed is in revolutions per minute (RPM).
- Use the equation: Input your torque and RPM values into the equation HP = Torque x Speed (RPM) / 5252.
- Calculate: Perform the multiplication of torque by RPM, dividing the result by 5252.
Example
Suppose an engine produces 300 lb-ft of torque at 2000 RPM. To find the horsepower:
HP = 300 x 2000 / 5252 = 600000 / 5252 = 114.15
Thus, the engine produces approximately 114.15 horsepower at 2000 RPM.
Fields/Degrees It Is Used In
- Automotive Engineering: Understanding the power output of engines.
- Aerospace Engineering: Designing efficient propulsion systems.
- Mechanical Engineering: Machine design and power transmission systems.
- Marine Engineering: Calculating power for ship propulsion.
- Renewable Energy: Designing wind turbines and other rotating machinery.
Real-Life Applications
- Vehicle Performance Tuning: Modifying engines to achieve desired horsepower.
- Wind Turbine Design: Calculating the power output based on wind speed and turbine characteristics.
- Electric Motors: Designing motors for specific torque and speed requirements.
- Determining Fuel Efficiency: Estimating engine efficiency and fuel consumption.
- Power Generation: Planning and design of generators and turbines.
Common Mistakes
- Wrong Units: Not converting torque to lb-ft or speed to RPM.
- Math Errors: Incorrectly multiplying or dividing, especially under time pressure.
- Misapplication: Using the equation where variables are outside their applicable range (e.g., extremely high speeds not typical in practical applications).
- Overlooking Variable Torque: Assuming torque stays constant across different speeds.
- Ignoring Efficiency Losses: Not considering that actual power output may be less due to mechanical inefficiencies.
Frequently Asked Questions
- Can I use this equation for any engine or machine?
Yes, as long as you are dealing with rotational power, torque in lb-ft, and speed in RPM, this equation is applicable. - Why is 5252 used in the equation?
The number 5252 comes from unit conversions and the definition of horsepower. It balances the equation to give accurate horsepower calculations. - What if my torque is in Newton-meters?
You'd first need to convert Newton-meters (Nm) to pound-feet (lb-ft) by multiplying the Nm by 0.73756 before using it in the equation. - Does this apply to electric motors?
Yes, this equation applies to electric motors when calculating power output in terms of rotational speed and torque. - How do efficiency losses affect horsepower?
Efficiency losses mean that only some calculated horsepower is usable for work. Factors such as friction and heat loss reduce the actual output, and these losses should be considered for precise engineering applications.
Online Web Apps, Rich Internet Application, Technical Tools, Specifications, How to Guides, Training, Applications, Examples, Tutorials, Reviews, Answers, Test Review Resources, Analysis, Homework Solutions, Worksheets, Help, Data and Information for Engineers, Technicians, Teachers, Tutors, Researchers, K-12 Education, College and High School Students, Science Fair Projects and Scientists
By Jimmy Raymond
![]()
Contact: [email protected]
Privacy Policy, Disclaimer and Terms
Copyright 2002-2015